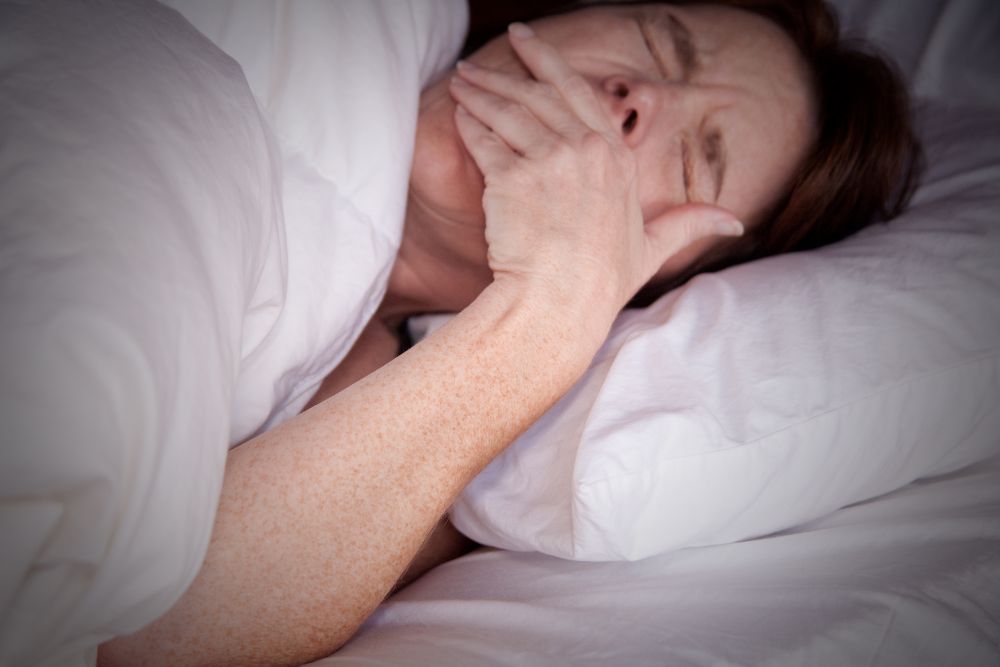
Menopause often causes changes that can negatively impact your sleep pattern. Sleep disorders associated with hormonal changes during menopause are common. Factors that influence sleep disturbances include fluctuation of hormones, nocturnal hot flashes, and psychological symptoms, such as mood changes.
Insomnia
Insomnia involves trouble getting to sleep, staying asleep, or maintaining restorative sleep. Restorative sleep includes two sleep phases called deep sleep and REM. Although all sleep is considered good, restorative and REM sleep stages contribute to the most mentally and physically restorative sleep. Changes in hormones, such as a decrease in estrogen levels, are linked with insomnia during menopause.
Night Sweats
It is common for women to experience night sweats during menopause. Night sweats are hot flashes characterized by sudden warmth, usually involving the neck, face, and chest. Hot flashes can cause profuse sweating and a sense of anxiety. Night sweats typically disrupt a person’s sleep, causing frequent wakefulness during the night.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a severe sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly pauses and begins again while a person sleeps. Sleep apnea can occur during any stage of life. But, when it happens during menopause, sleep apnea is often caused by weight gain and lower estrogen and progesterone levels. Often, sleep apnea caused by menopausal hormone changes goes undiagnosed because many people attribute the symptoms, such as daytime fatigue, directly to menopause.
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is a neurological condition. Symptoms of RLS include an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by discomfort. RLS can disrupt nighttime sleep. Menopause has been found in clinical trials to increase the severity and prevalence of RLS symptoms.
Emotional Factors
Stress and emotional factors can negatively impact sleep quality. Hormonal changes that occur during menopause are linked with anxiety and depression. These emotional changes are known to contribute to sleep disturbances.
Sleep-Disordered Breathing
During menopause, hormonal changes can affect respiratory control, causing sleep-disordered breathing, such as snoring, sleep apnea, and other breathing problems.
Sleep Architecture Changes
Sleep architecture is affected by menopause, including changes in rapid eye movement (REM) and non-REM sleep patterns.
Menopausal Sleep Disorders: Management
Lifestyle Modifications
Several lifestyle modifications can help you get a restful night’s sleep, including:
- Establish a consistent sleep routine to help regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Maintain a cool, dark, comfortable sleep environment.
- Don’t drink alcohol before bedtime (alcohol interferes with healthy sleep patterns)
- Avoid computer, smartphone, and television screen time before bedtime (blue light emitted by screens can interfere with melatonin [the sleep hormone] production)
- Engage in meditation or relaxation techniques known to help improve sleep
- Avoid greasy, heavy meals, nicotine, and caffeine before bedtime. These foods and substances may disrupt sleep.
- If noise is a problem, consider using a white noise machine or using earplugs while sleeping.
Consider Seeking Individualized Treatment
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage menopause symptoms, such as insomnia or hot flashes. One such is hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can help alleviate menopause symptoms, including sleep disturbances.
If you are experiencing sleep disturbances during menopause or other uncomfortable menopause symptoms, you may consider consulting one of our caring, experienced gynecologists at Pacific Gynecology & Obstetrics Medical Group. We can identify the specific cause of your sleep issues and recommend an individualized treatment plan based on your needs and circumstances.